Optimized LM-LAD PCI with IVUS and FFR Guidance
By: Dr. Aninka Saboe

patient history
49-year-old male, CCS II
History of extensive anterior wall STEMI two months prior, treated with balloon angioplasty at ostial LAD (deferred stenting)
Cardiovascular risk factors: Type II diabetes mellitus, ex-smoker
Echocardiography: LVEF 65%, normal wall motion
Laboratory: Hb 13.3 g/dL, eGFR 99 ml/min/1.73m²
Case Challenges
Need to assess both LM and LAD disease severity and plan optimal intervention
Decision-making for side branch (LCX) treatment in the setting of LM bifurcation disease
Techniques used
Pre-PCI FFR measurement to assess functional severity
IVUS to guide lesion assessment, landing zone selection, and stent sizing
Key learnings
IVUS could assist in avoiding pitfalls and also optimizing results in LM PCI
To date, there are no guidelines regarding the most appropriate approach for SB intervention in LM PCI; therefore, FFR could help determine the strategy.
Procedure
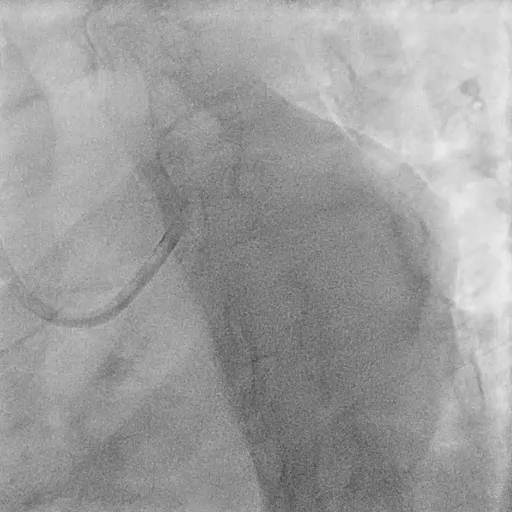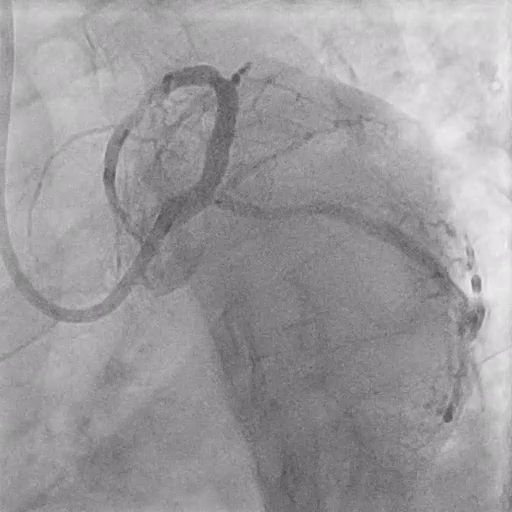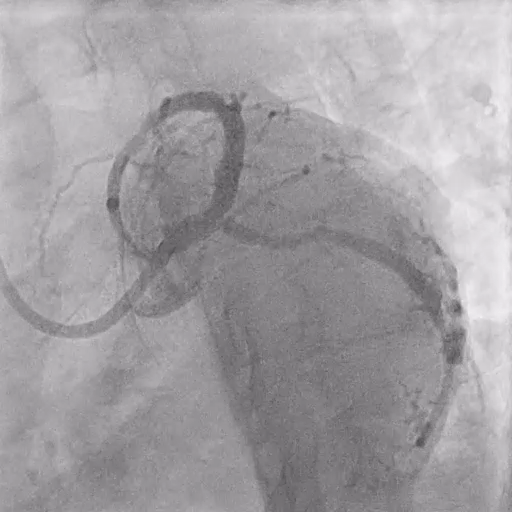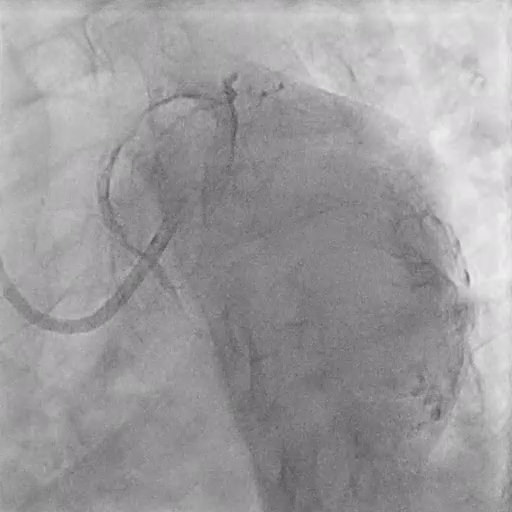
Pre-LM-LAD PCI:
FFR at LAD: positive (0.60)

IVUS findings:
Distal landing zone: EEM diameter 4.2 mm, plaque burden 35%
Ostial LAD: plaque burden 72%, MLA 2.9 mm²
Proximal landing zone: EEM diameter 5.2 mm, plaque burden 30%, fibrolipidic plaque morphology

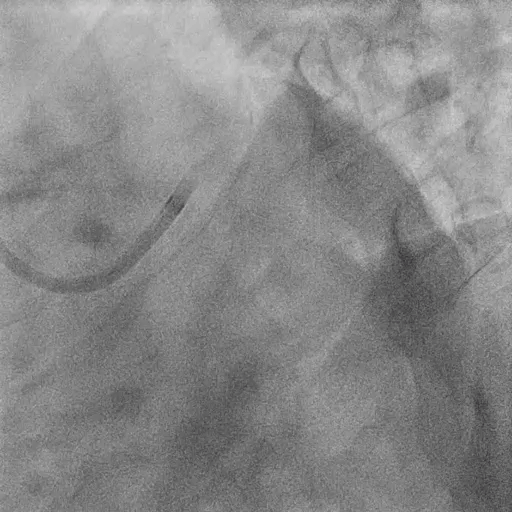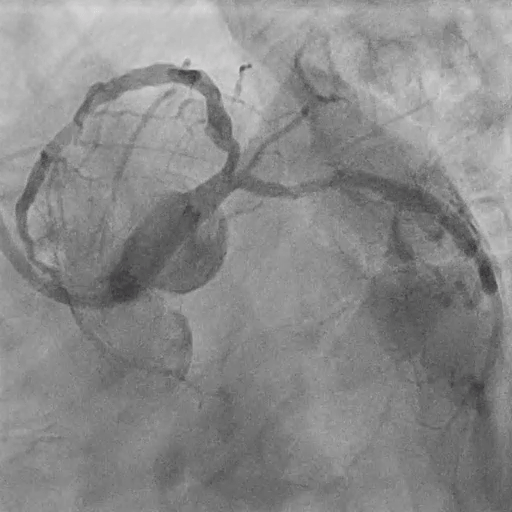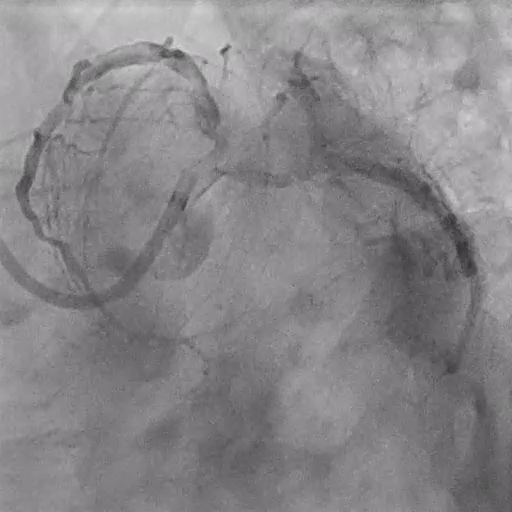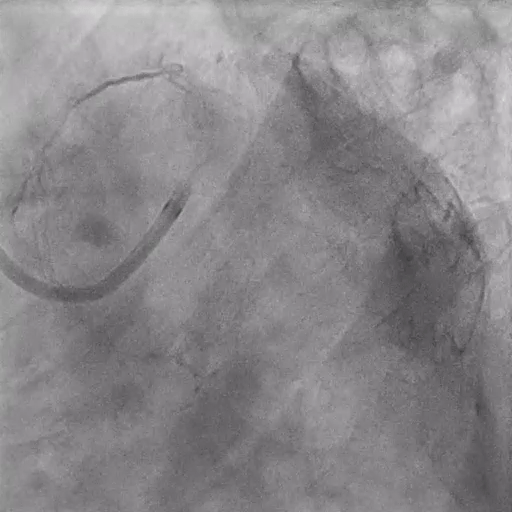
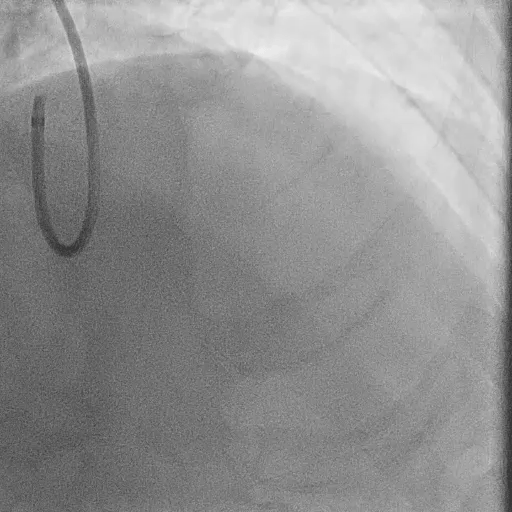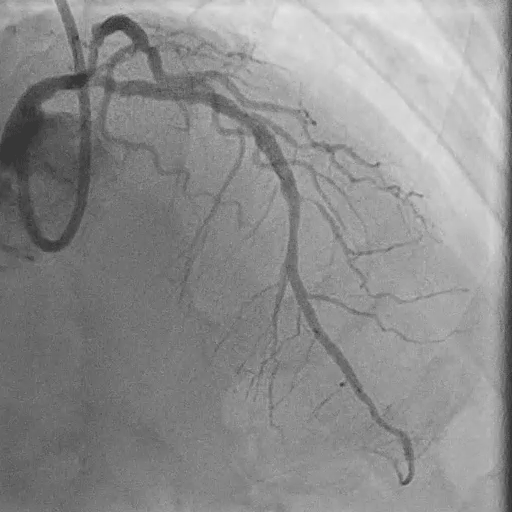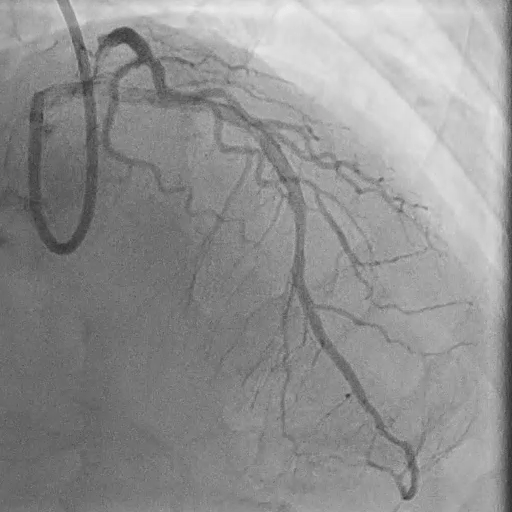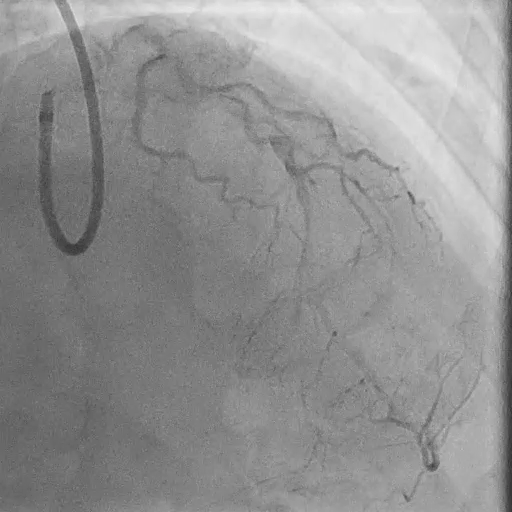
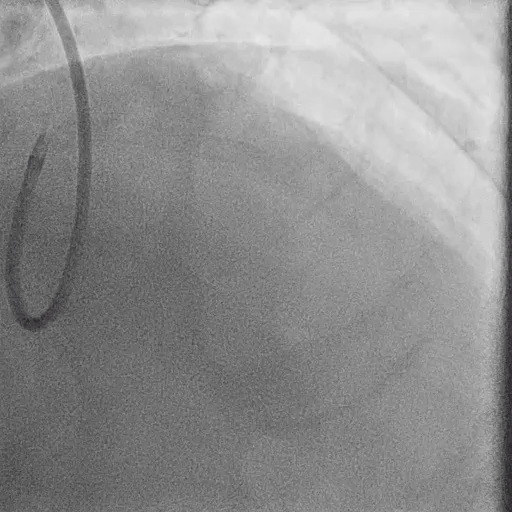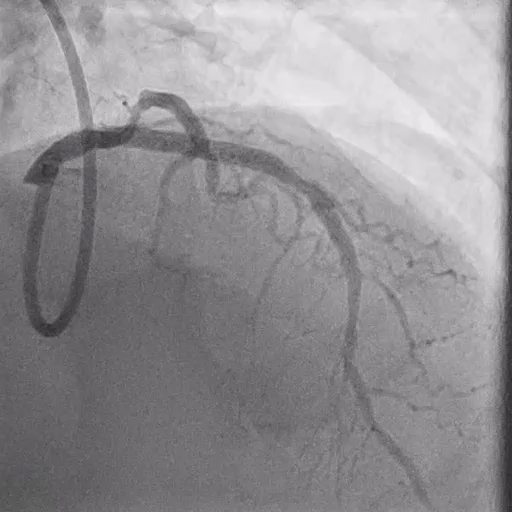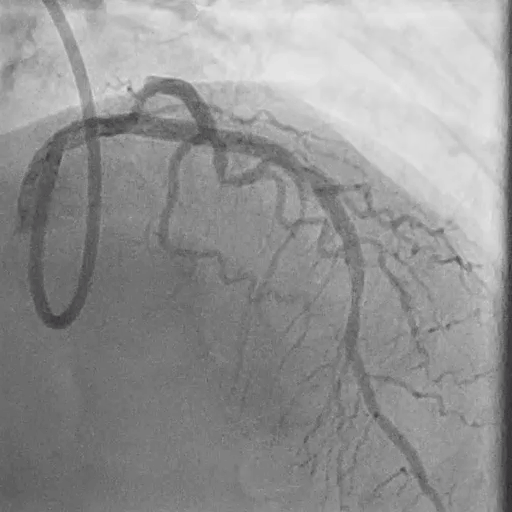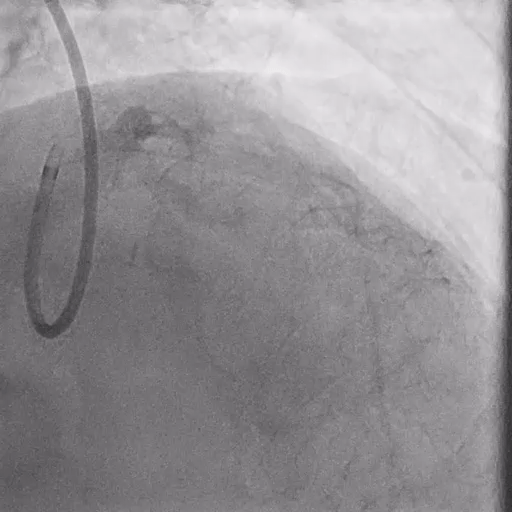
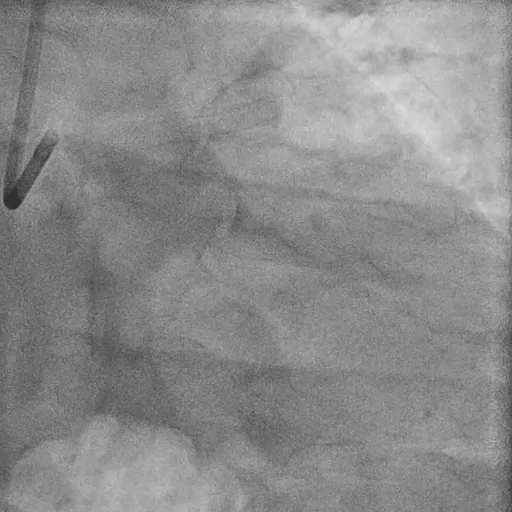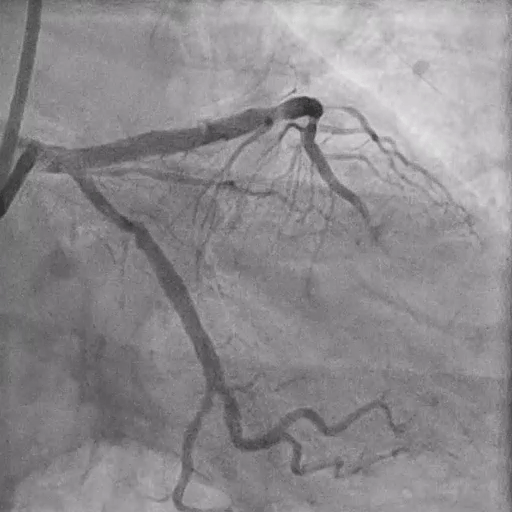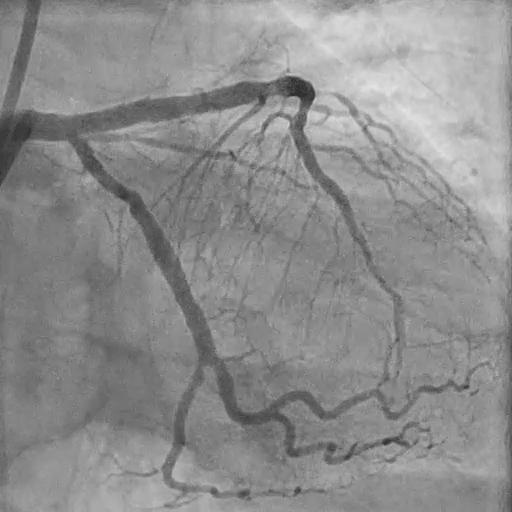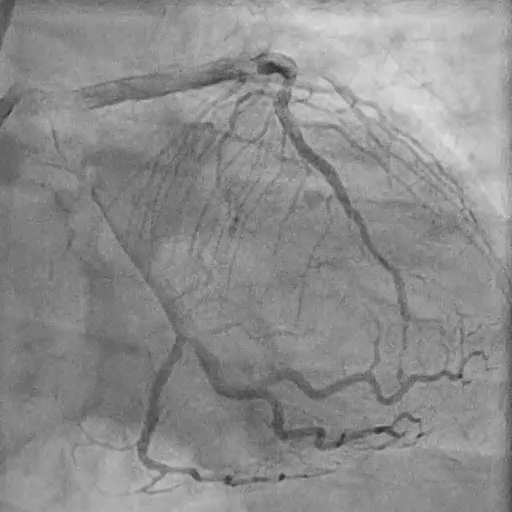
During LM-LAD PCI
Predilation with 4.0/15 mm NC Scoreflex balloon
Implantation of 4.0/34 mm DES from LM to LAD
POT with 5.0/15 mm NC balloon

LCX Assessment
Rewiring into LCX
FFR at LCX: negative (0.93) → no PCI required

Post LM-LAD PCI
IVUS: good stent apposition, no edge dissection, minimal overlying strut at Ostial LCx
MSA: LM 11.23 mm², POC 10.86 mm², Ostial LAD 9.94 mm²
Post-PCI LAD FFR: 0.93
Final Angiography
Excellent vessel expansion and blood flow
Summary
This case highlights the importance of IVUS and FFR in the precise planning and optimization of LM PCI. Careful imaging and physiological assessment helped avoid unnecessary interventions and achieved excellent procedural and functional results.