IVUS-Guided DK-Crush for Complex LM Bifurcation
By: Dr. Aninka Saboe

Left main (LM) bifurcation disease represents a high-risk coronary lesion subset requiring precise revascularization strategies. DK-crush is an established technique for complex bifurcation lesions, particularly when both branches are significantly diseased. This case highlights the use of IVUS-guided DK-crush PCI in a patient with complex LM bifurcation disease who refused CABG.
patient history
Age/Sex: 52-year-old male
Clinical Presentation: Chronic Coronary Syndrome
Referral: For LM PCI after refusal of CABG
Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Hypertension, smoker
Echocardiography: LVEF 60%, normokinetic at rest
Stress Nuclear Scan: Stress-induced ischemia in left coronary artery (LCA) territory; ischemic burden 16.3%
Laboratory Tests: Normal renal function
Case Challenges
Complex distal LM bifurcation involving ostial LAD and LCX
Diffuse disease extending into LAD and LCX
Techniques used
Imaging Guidance: Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS)
Strategy: DK-Crush two-stent technique
Optimization: Sequential high-pressure POT and Kissing Balloon Inflations (KBI)
Stent Optimization: Additional post-dilatations based on IVUS findings
Procedure
Pre-DK Crush PCI
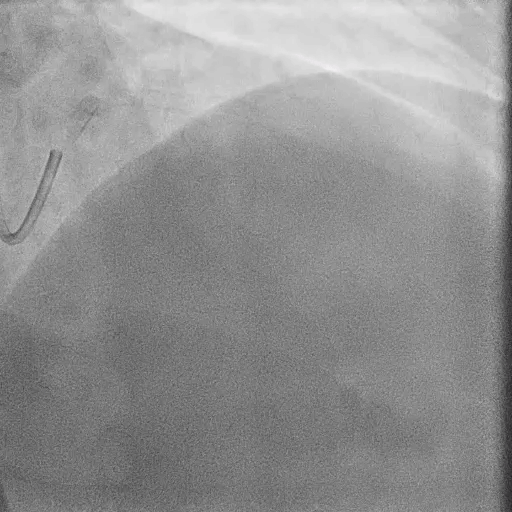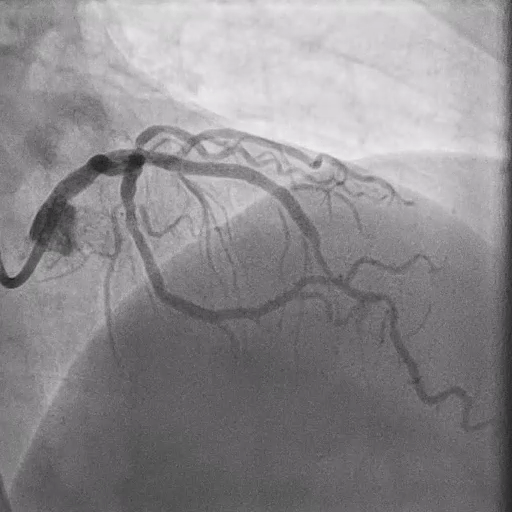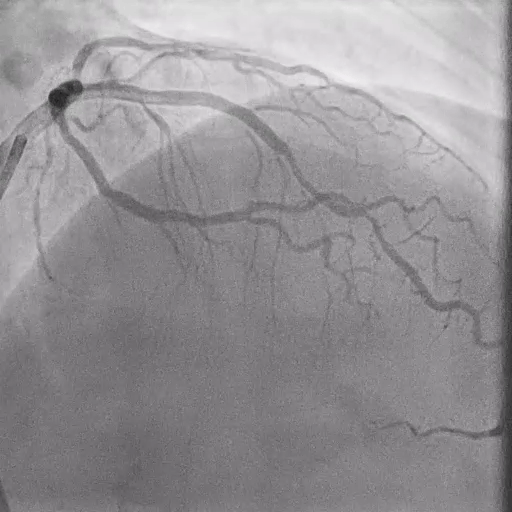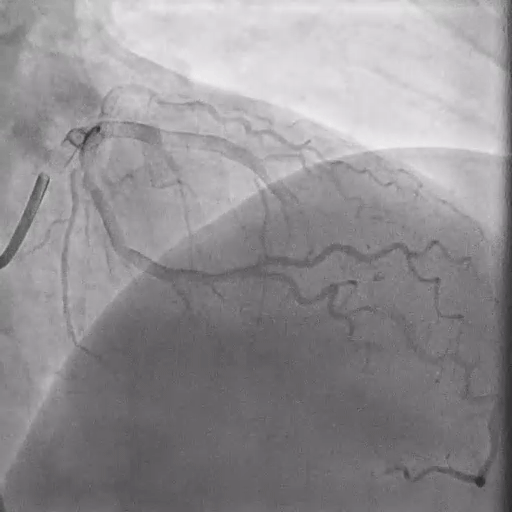
Identified severe stenoses at distal LM, ostial LAD, ostial LCX, LAD at ostial D1, LAD, and LCX.

After Predilation with 2.0 mm SCB, check IVUS at Distal LM, Ostial LCX, Ostial LAD, and LAD at Ostial D1 level.

Predialation at LM-LAD with 3.0/15 mm NCB (high pressure) and LM-LCX with 3.0/15 mm NCB (high pressure).
Due to dissection at Ostial-Proximal LCX, decided to perform 2-stent strategy (DK - crush).

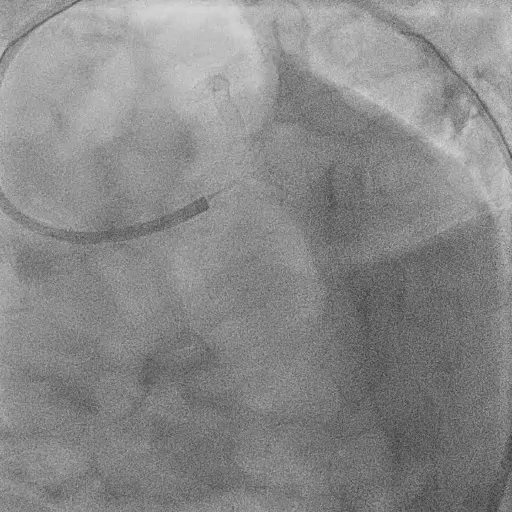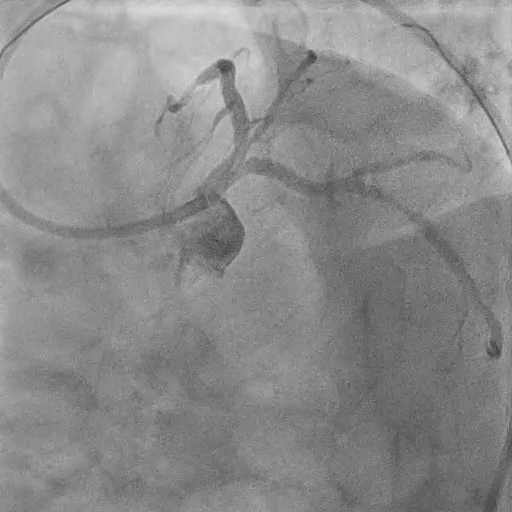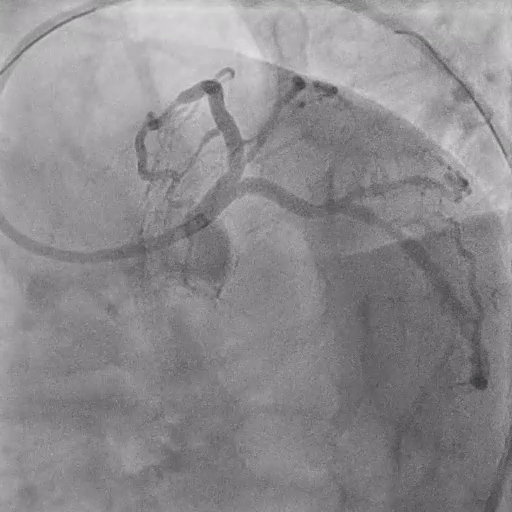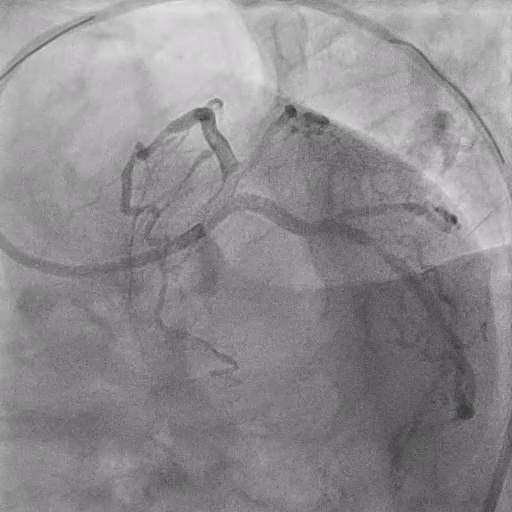
During DK-Crush PCI
Stenting:
3.0/34 mm DES placed at mid-distal LAD.
3.0/18 mm DES placed at proximal LCX with slight protrusion into LM.

Crushing and Rewiring:
Balloon crush with 4.5/10 mm NCB followed by POT.

Check crushed stent, proximal crossing point, and SB rewiring transition with IVUS.

First KBI performed with 3.5/15 mm NC (LM-LAD) and 3.0/15 mm NC (LM-LCX). Second DES (4.0/26 mm) deployed at LM-LAD.

Optimization:
POT with 4.5/10 mm NCB, rewire LCX, verify with IVUS.


Second KBI and final POT.

Post-DK Crush PCI
IVUS Findings:
Check the MSA at Ostial LAD and MSA at Ostial LCX with IVUS. Find underexpansion at Ostial LAD.

Use 3.5/15mm NC at LM-LAD and 3.0/15mm NC at LM-LCX for stent optimization.
Final results: Check the final DK crush results with IVUS. MSA: LM 12.1mm2, POC 11 mm2, Ostial LAD 8mm2, Ostial LCx 7.1 mm2
Key Learnings
IVUS guidance is crucial in complex LM bifurcation PCI to ensure optimal stent sizing, expansion, and positioning.
DK-crush technique provides excellent scaffolding and coverage for complex LM bifurcation lesions.
Multiple rounds of POT and KBI are often necessary to optimize outcomes in challenging anatomies.
Real-time IVUS assessments allow immediate identification and correction of suboptimal stent deployment.